Reference of the picture: Decontamination Archive Site
Hello, everyone. My name is Daichi, an expert providing the information on the radiation issues in an easy-to-understand manner.
During the decontamination works, generated soil and waste (waste mainly comprises of organic matter such as leaves and branches) (‘generated soil and waste’ hereinafter is referred to as ‘removed soil and waste’) are usually temporarily stored in temporary storage sites for a while until they are further transported to the next procedure.
Regarding the temporary storage sites, this article responds to the following question.
– What is the structure of the temporary storage sites used in the decontamination project?
Table of contents of this article
- (Let’s learn basic structure) Management of temporary storage sites (Vol. 1)
- Basic structure of a temporary storage site
- Fence
- Sign
- Water drain
- Container bag
- Shielding bag
- Cover sheet
- Water collection pipe and tank
- Weight and bottom sheet
- Monitoring well of underground water
- Summary
I have been involved with the radiation-relevant issues, like the policy on the decontamination activities and the management of the Interim Storage Facility, after the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011.
I received a doctorate in the field of radiation, while working in Fukushima.
(Let’s learn basic structure) Management of temporary storage sites (Vol. 1)
The procedures of decontamination activities and treatment procedures of removed soil and waste are covered in this article and this article, respectively.
This article and this article elaborate temporary storage sites, which store temporarily the removed soil and waste, until they are further transported for the next procedure.
And this article explains key points, especially focusing on the structure of temporary storage sites used in the decontamination activities.
Basic structure of a temporary storage site
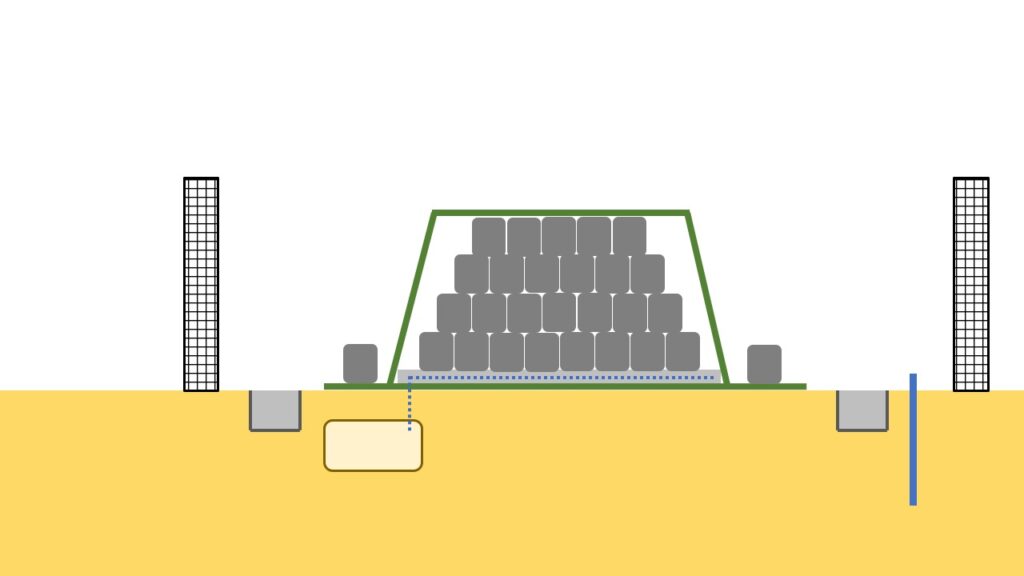
As covered in this article off-site remediation projects can be roughly categorized into 2 kinds of works: decontamination projects and treatment of the Specified Waste.
With regard to the Specified Waste, please refer to this article.
Temporary storage sites have been constructed for each kind of project, and there are some difference, e.g.: structure of the temporary storage sites.
This article covers the temporary storage sites used in the decontamination projects, especially focusing on the basic structure, based on the above figure.
Fence
First of all, fences surrounding the temporary storage sites.
This is something to prevent from intentionally and unintentionally intruding into the premise of the temporary storage sites.
Not only people, but also wild animals like wild boars sometimes come into the premise of the sites.
In order to protect facilities from damage caused by the intrusion, fences are set in advance, and they are sometimes net fences as shown in the following figure, but sometimes they are wooden piles and steel lines, or steel panels.
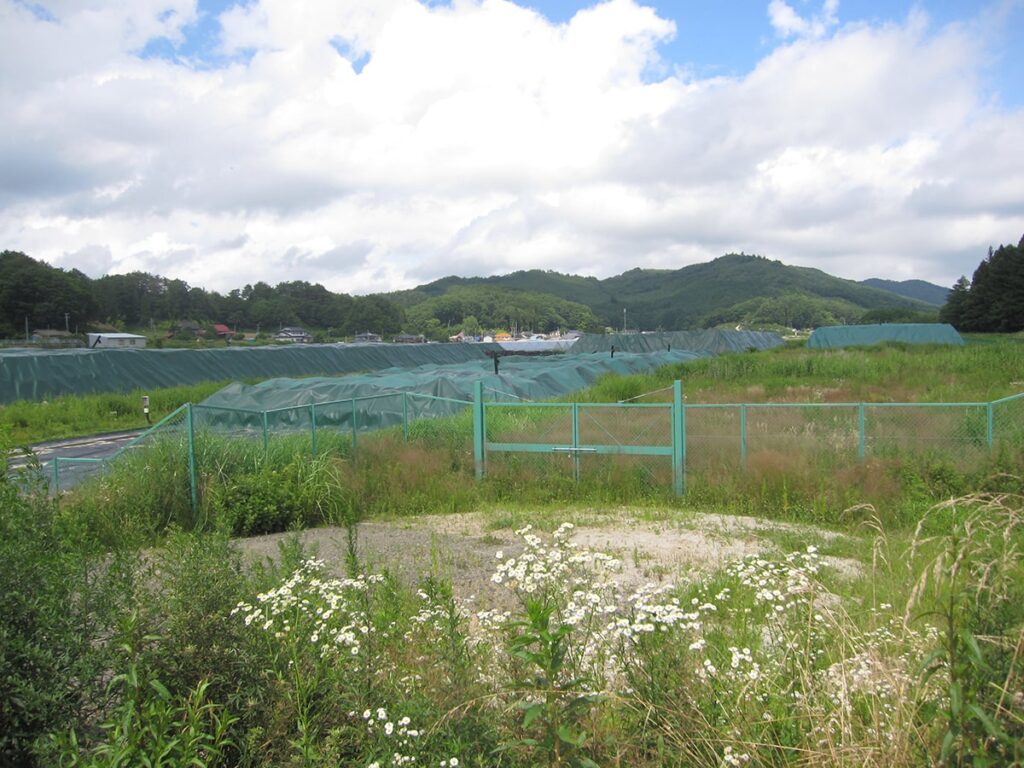

Reference of the picture: Decontamination Archive Site
Sign
Usually a sign is on fences or gates at entrance of the temporary storage sites.
Name, kinds of stored waste, an emergency phone number and other necessary information are written on the sign.
In addition, together with the sign, the result of periodical monitoring of air dose rate is usually shown, although it will be covered in this article.

Reference of the picture: Decontamination Archive Site
Water drain
In most cases premises of the temporary storage sites are originally farmland and they are not paved, therefore, sometimes land erosion occurs and puddles could be left after rainfall, which could affect management of the temporary storage sites.
Therefore, water drains with slope (gradient) are installed so that rainwater that falls on the premises of the temporary storage sites can be quickly drained outside the premises.
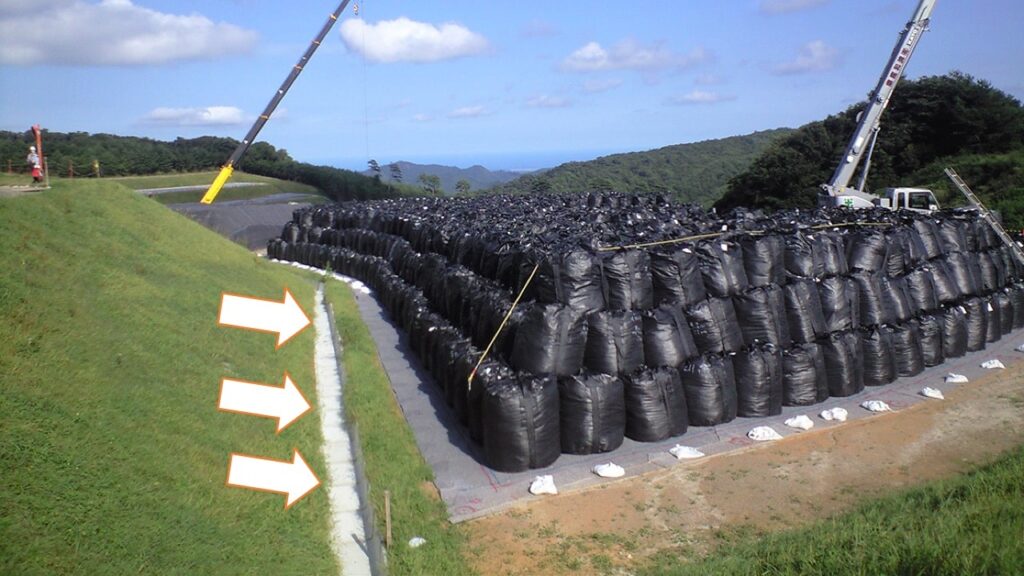

Reference of the picture: created based on the Decontamination Archive Site
Container bag
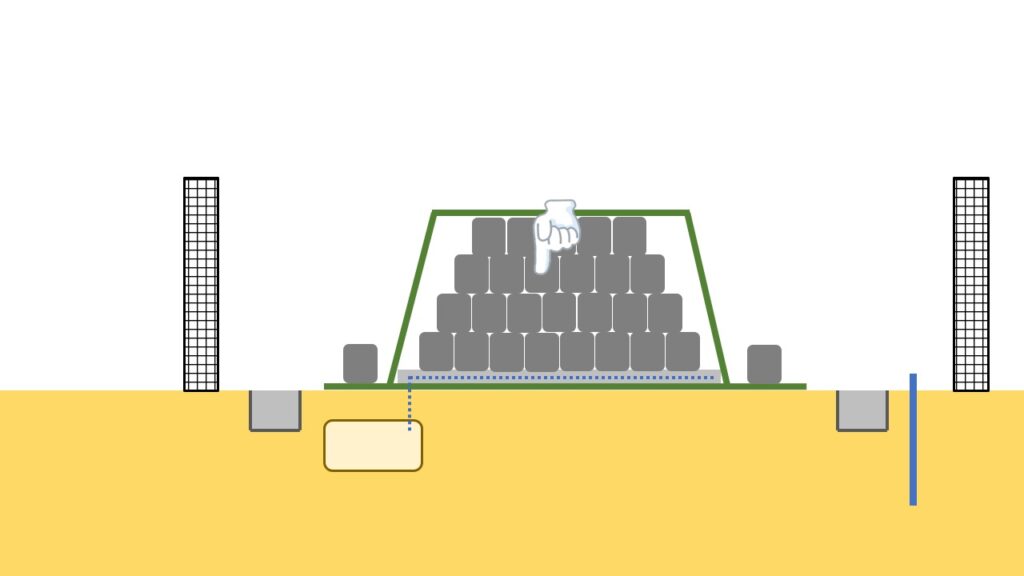
Next, container bag to store soil and waste arising from decontamination activities.
The container bag is sometimes called in a variety of different names, such as ‘Flexible container’, or ‘Ton bag’, for example, in news.
In addition, it is not still well-known, but sometimes it is called ‘Weather-resistant large-size sand bag’.
There are different ways for the categorization of container bag:
– Regarding the ‘Flexible container’ as a general name and ‘Weather-resistant large-size sand bag’ as one of the flexible containers, and
– Regarding the ‘Container bag’ as a general name and differentiate ‘flexible container’ with ‘Weather-resistant large-size sand bag’, because standard of each kind of bag is determined by each different association.
This article hereinafter adopts the latter:’Container bag’ is a general name and ‘flexible container’ and ‘Weather-resistant large-size sand bag’ are examples of the container bag).
Reference: Web sites of the Japan Flexible Container Industry Association and the Japan Weather-resistant Large-size Sand Bag Association (in Japanese).
Initially permeable container bags, which let rainfall pass through inside the container bags, were used shortly after decontamination activities started, but gradually they have been replaced with impermeable container bags, with one or double inside the container bags, during progress of decontamination activities.
With this replacement, container bags have not let rainfall go into the container bags, that made it unnecessary for the water collection pipes and tanks to be used anymore, and permeable cover sheets have been replaced with permeable sheets to protect the container bags from sunlight, which will be touched upon in the following parts of this article.
These changes in structure have made management of temporary storage sites much easier than previous days.
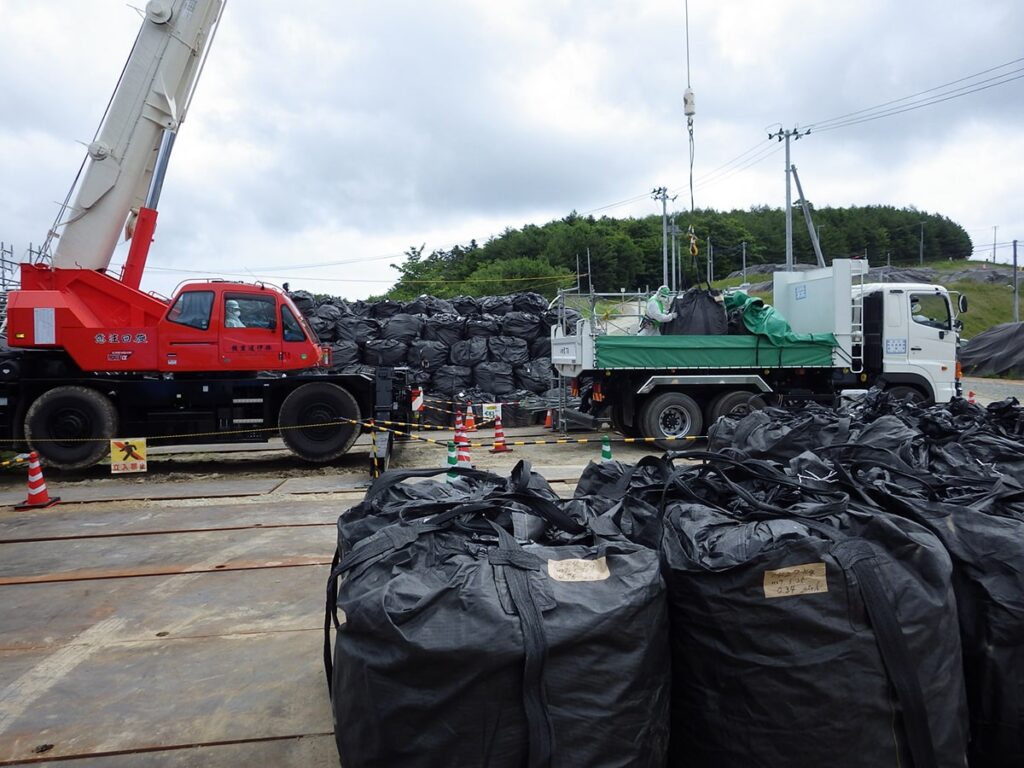

Reference of the picture: Decontamination Archive Site
Shielding bag
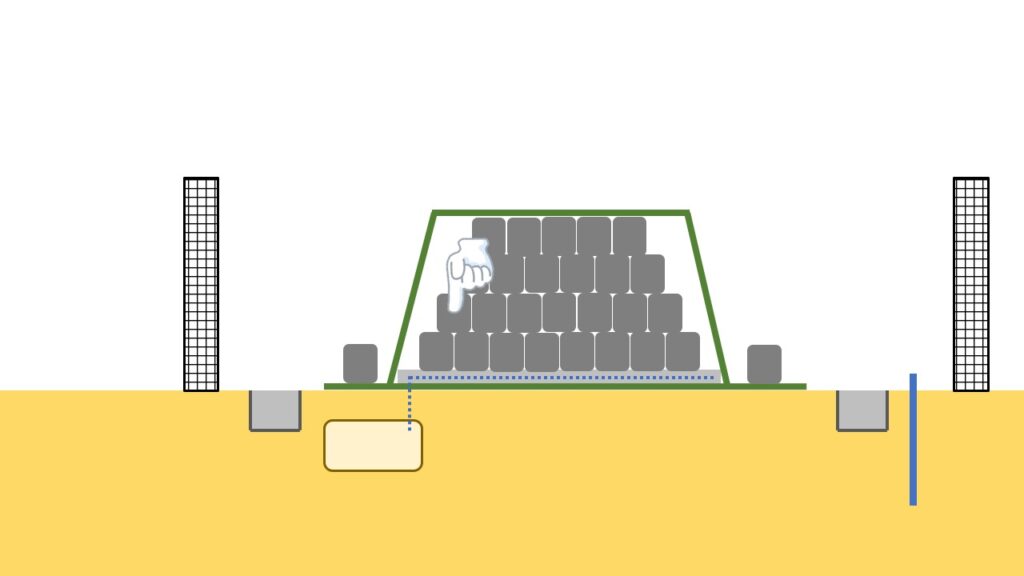
At temporary storage sites, the size of piles (unit groups of container bags) is designed, taking account of the length of the crane arm so that the above-mentioned container bags can be transported out even in the event of an emergency.
The inside of the pile is structured as shown in the figure below, with the removed soil and waste stored in the middle, and the surrounding part is shielded with soil which was not generated during the decontamination activities, such as sand in mountains.
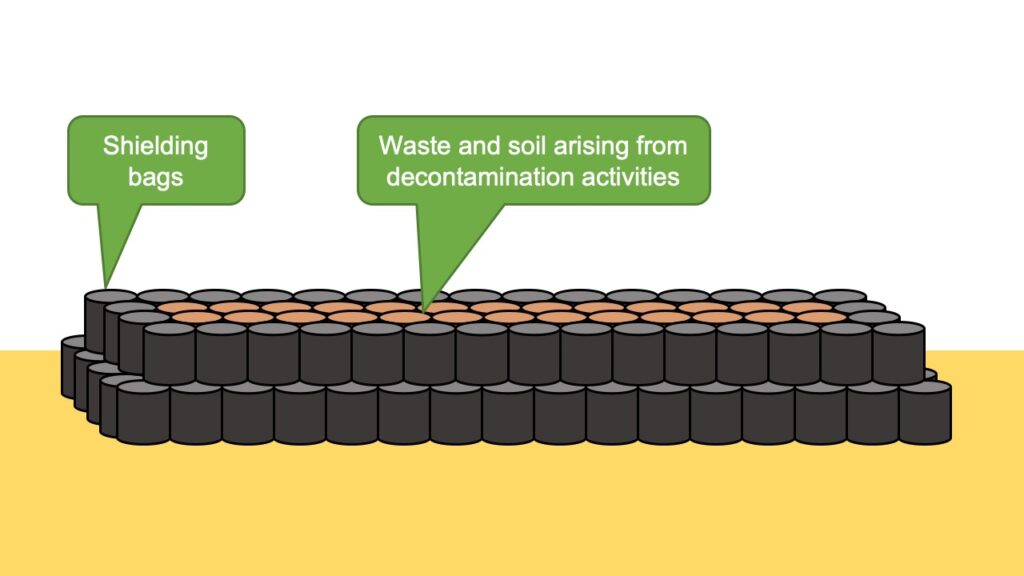
This is a measure to reduce the impact of radiation emitted from removed soil and waste on the surroundings as much as possible.
With this measure, it is possible to minimize the dose of workers who manage the temporary storage sites after their construction, but at the same time, a large amount of shielding bags will remain after the removed soil and waste are carried out.
The temporary storage sites are lands which are temporarily rented from the land owners, so they will eventually have to be returned to the owners. As a result, securing destinations for their reuse will become a challenging issue.
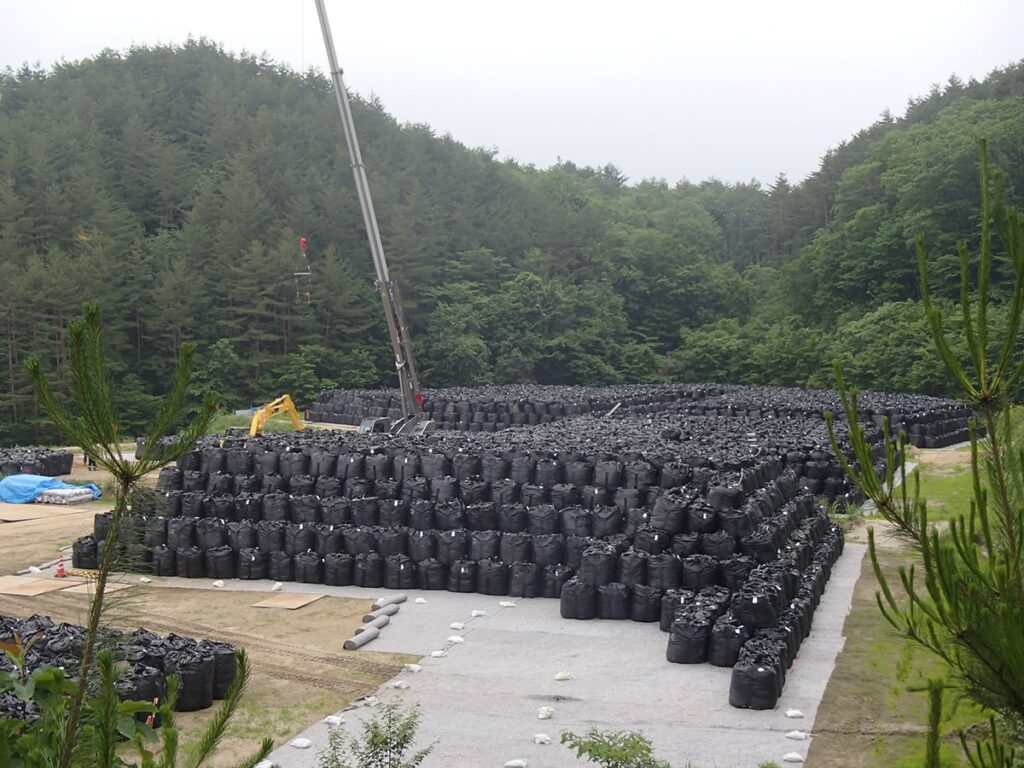

Reference of the picture: Decontamination Archive Site
Cover sheet
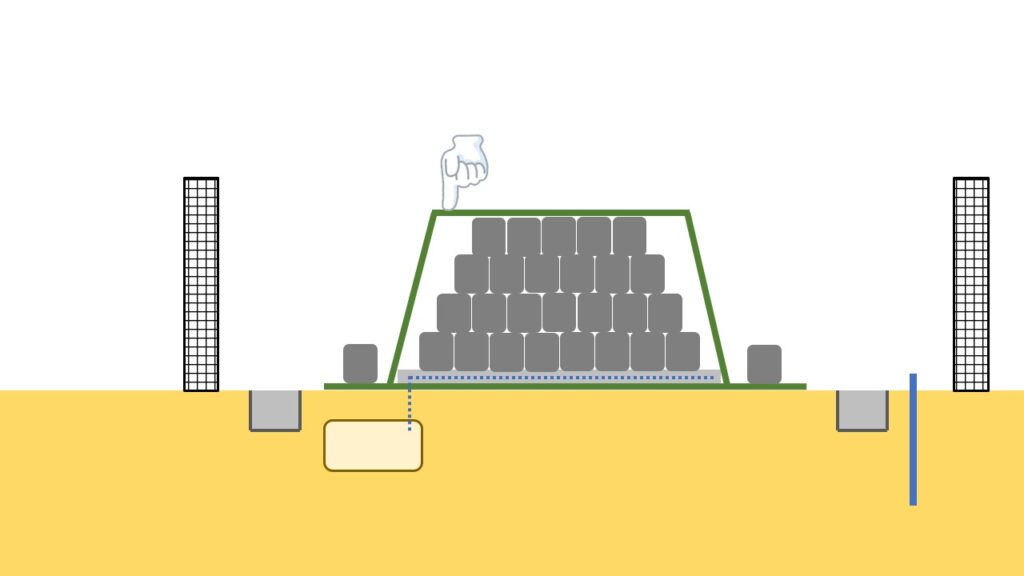
Along with the improvement of container bags mentioned above, changes were also able to be seen in the cover sheets.
Initially, as mentioned above, the container bags were permeable, which allowed rainwater to pass through, so impermeable cover sheets were used to prevent rainfall from penetrating into the piles.
When storing organic matters such as branches, leaves, and grass, water-impermeable but air-permeable sheets were sometimes used to prevent flammable gases generated through fermentation from accumulating inside the piles.
However, if water-permeable sheets are used, of course, puddles will remain at the top of the piles, which will put a load on the piles and sometimes generate mosquitoes in the summer. There were also disadvantages, such as the need to treat the water, which sometimes comes into the piles.
After that, as mentioned above, the container bags were improved and replaced with container bags which don’t allow water to pass through, then the cover sheets were also replaced with those which allow water to come into the piles.
This change has greatly reduced water treatment and makes it easier to manage the temporary storage sites.
Some may think that if water does not come into the container bags, it is not necessary to cover them with sheets, but this is still necessary to prevent the container bags from being exposed directly to sunlight.
If the container bags are exposed to sunlight for a long period of time, they will inevitably deteriorate faster.
In order to prevent this from happening, a light-shielding sheets are still necessary (‘Shakou Sheet (「遮光シート」 in Japanese) in the photograph below means a sheet which lets water come into the piles but just shields sunlight’).
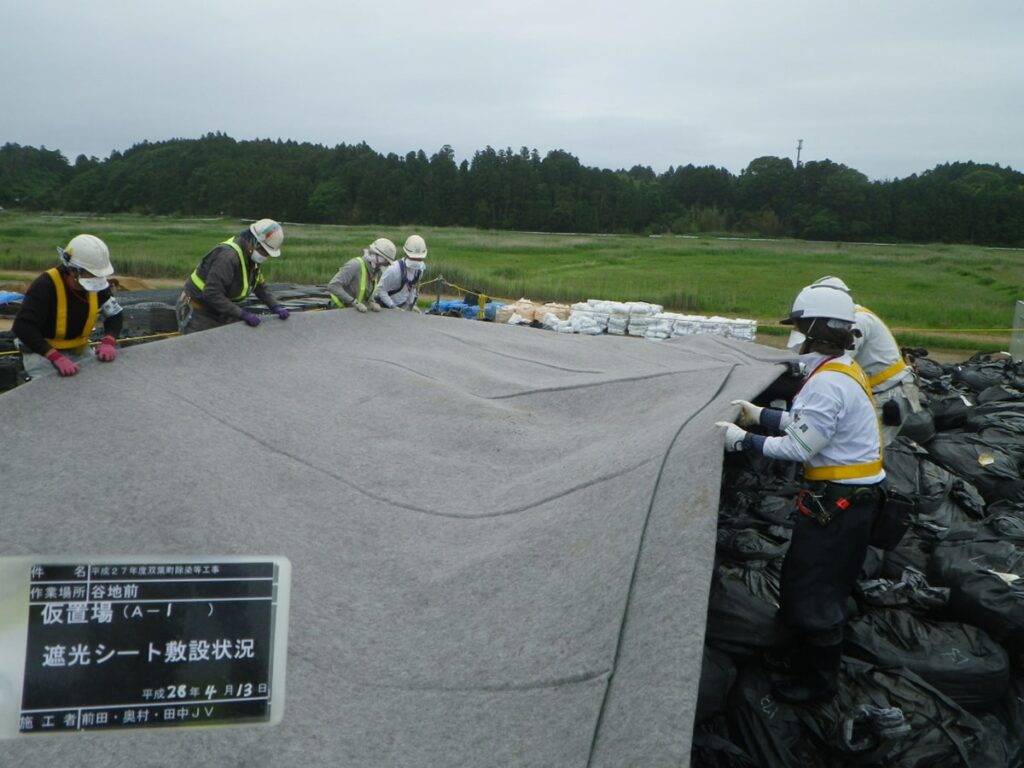

Reference of the picture: Decontamination Archive Site
Water collection pipe and tank
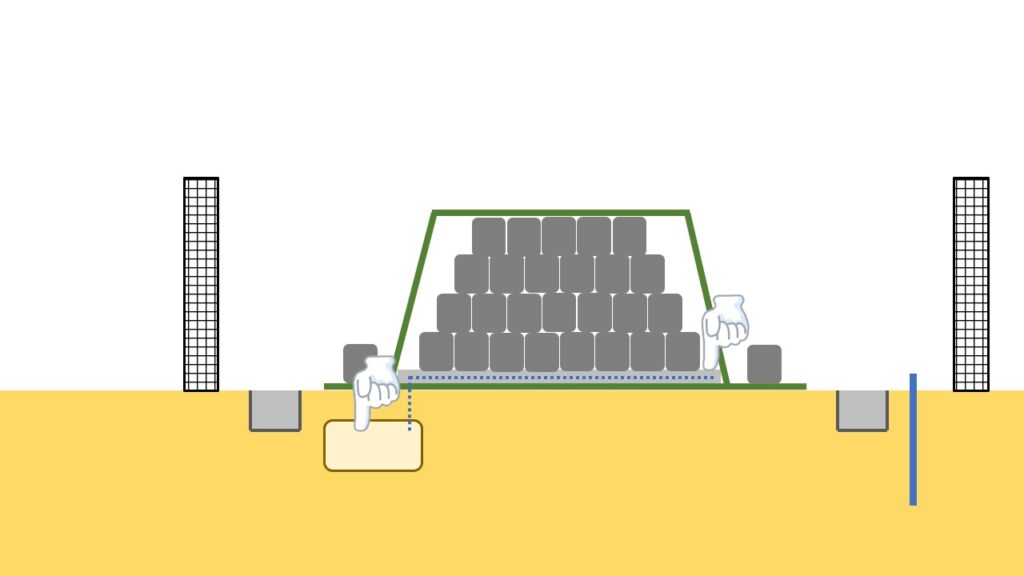
Water collection pipe and water collection tank are equipment for collecting water which accumulate inside the pile.
As explained several times, when water permeable container bags were used, the water collection pipe and tank were installed and water level in the tank was periodically checked, and radioactivity concentration of water in the tank was also measured periodically.
Since after container bags were gradually changed into water impermeable bags, which don’t allow water to pass through, these equipment has become unnecessary.
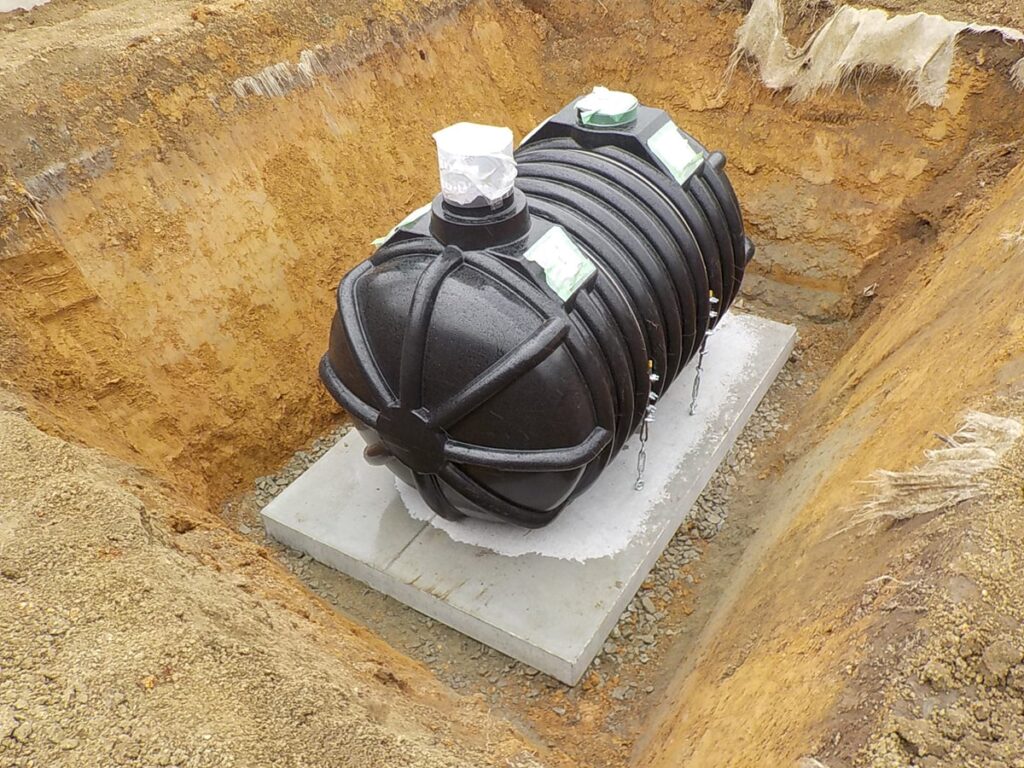

Reference of the picture: Decontamination Archive Site
Weight and bottom sheet
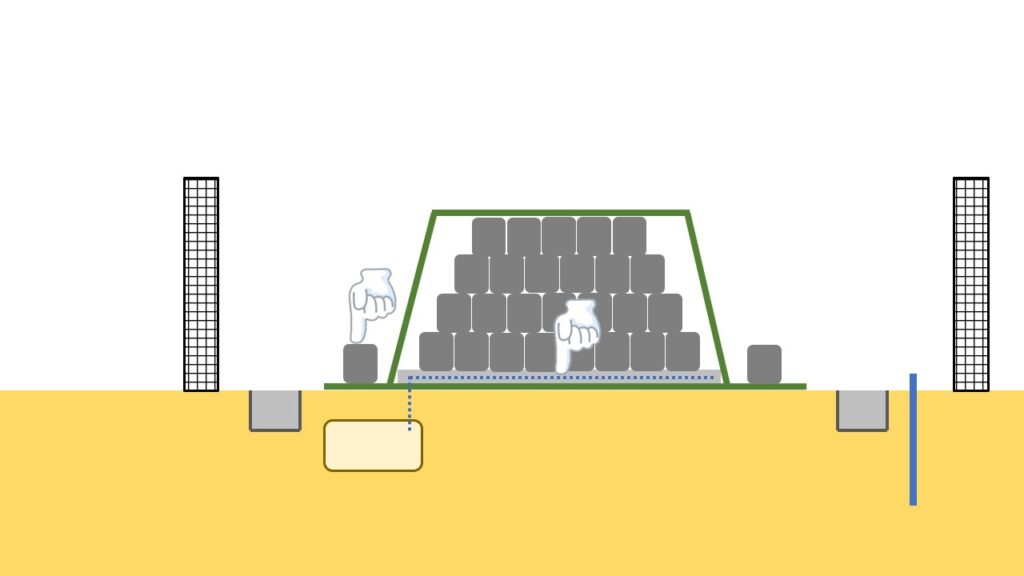
A bottom sheet is laid at the bottom of the pile where the removed soil and waste are stored, and as shown in the photo below, the sheet is further sandwiched between mats for its protection.
By the way, when the water permeable container bags were used, it played a role to prevent the water inside the pile from leaking out to the outside.
Even after the container bags have been changed into water impermeable types, which don’t allow water to pass through, the bottom sheet has been used, to prevent direct contact with the ground underneath that could cause damage on the container bags.

Reference of the picture: Decontamination Archive Site
Monitoring well of underground water
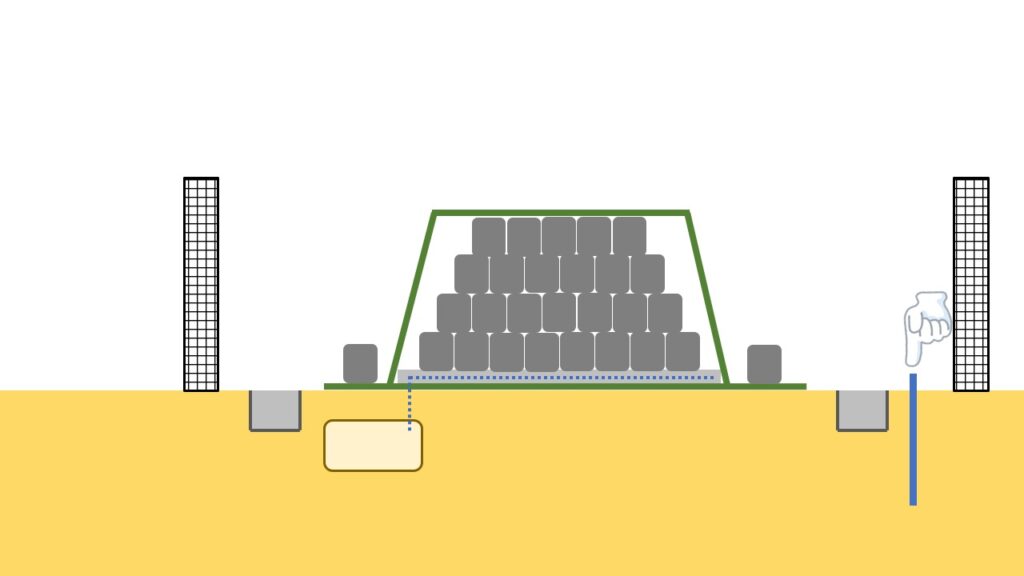
The last facility to be introduced in this article is monitoring well of underground water.
This is installed in the downstream of water flow in every temporary storage site, and even if radioactive materials contained in removed soil and waste leak into groundwater, the radioactive materials can be monitored using the well.
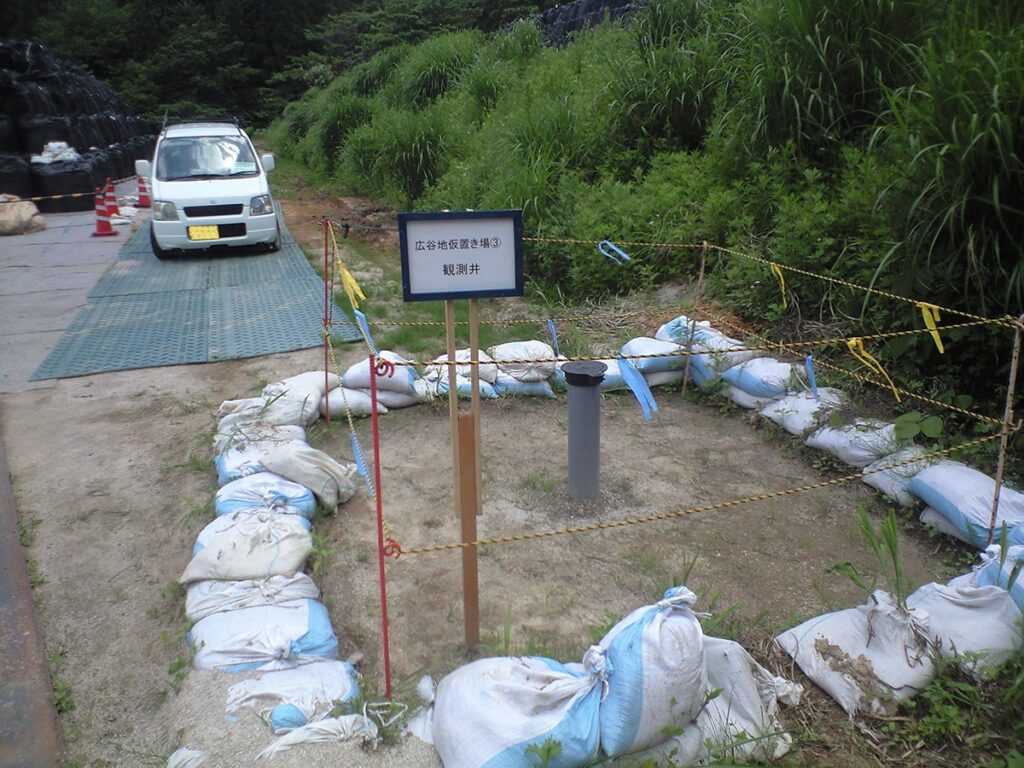

Reference of the picture: Decontamination Archive Site
Summary
This article covers temporary storage sites used in the decontamination activities, especially focusing on their structure.
In the Fukushima Prefecture, large-scale transportation projects to the Interim Storage Facilities were completed by the end of fiscal year 2021 (March 2022), except for the Difficult-to-Return Zones.
Regarding the evacuation areas, please visit this article as well as this article.
As a result of progress of the projects, the number of the temporary storage sites has decreased in a step-by-step manner, and restoration projects of the temporary storage sites into original paddy fields and other kinds of land are currently in progress.
The Interim Storage Facilities are elaborated in this article, this article, this article and this article.
By the way, above-mentioned contents are summarized in the following videos.
It would be appreciated to visit them at your convenience.
– Japanese version
– English version
You can read the same article in Japanese here.
Thank you very much for reading this article.
See you next time!



コメント