Hello, everyone. My name is Daichi, an expert providing the information on the radiation issues in an easy-to-understand manner.
Today, I would like to respond to the following questions:
– How can negative impacts on human health caused by exposure to radiation classified?
– What are the ‘deterministic effects’ and ‘stochastic effects’?
– What is the mechanism to cause the deterministic effects?
Table of contents of this article
- Impact on human health caused by exposure to radiation (Vol. 1)
- Classification of impacts caused by exposure to radiation
- What are the ‘deterministic effects’ and ‘stochastic effects’?
- The deterministic effects
- The stochastic effects
- Mechanism to cause the deterministic effects
- What is the threshold value?
- Summary
I have been involved with the radiation-relevant issues, like the policy on the decontamination activities and the management of the Interim Storage Facility, after the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011.
I received a doctorate in the field of radiation, while working in Fukushima.
Impact on human health caused by exposure to radiation (Vol. 1)
What kind of approaches for classification can be considered for impact on human health caused by exposure to radiation?
Let us begin with this theme in the following sections.
Classification of impacts caused by exposure to radiation

There are a couple of approaches for classification of impact on human health caused by exposure to radiation such as:
– Entity to be made impacted by radiation (himself/herself or their offsprings)
– Incubation period until the impacts actually appear on human body (immediately after the exposure, or after some time passes)
– Mechanism which causes impact on human health
This article basically covers all the above 3 kinds of classification, but especially is based on the third category: mechanism which causes impact on human health.
What are the ‘deterministic effects’ and ‘stochastic effects’?
When the impacts on human health caused by exposure to radiation are classified, focusing on the mechanism to cause impact on human health, they can be roughly classified into ‘the deterministic effects’ and ‘the stochastic effects’.
In the following sections they will be elaborated in detail.
The deterministic effects
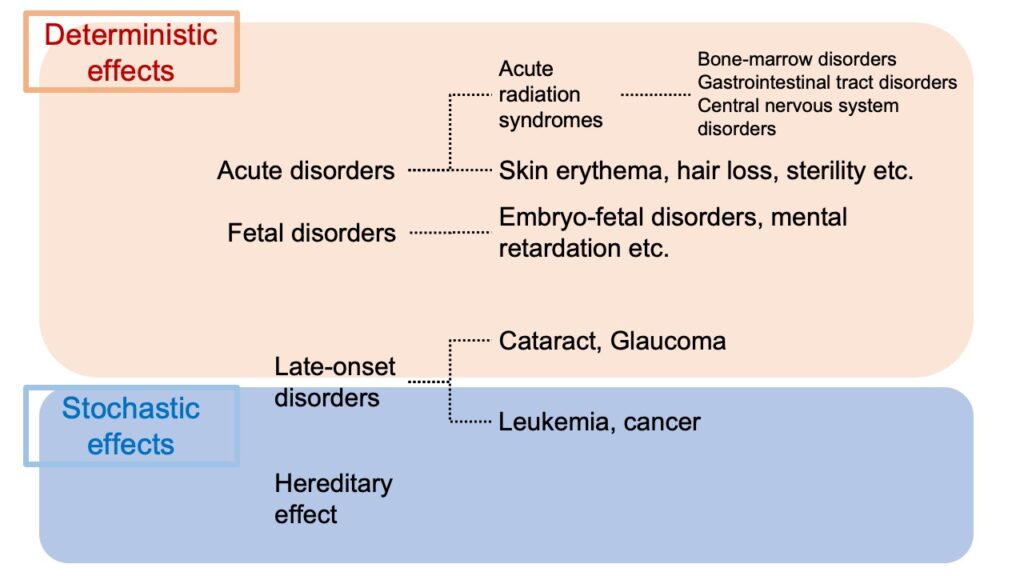
The deterministic effects appear when people are exposed to a relatively large amount of radiation, in a short period of time.
And as represented in the above figure, as an example of the deterministic effects on exposed people themselves, acute disorders can be taken, and sometimes disorders on the radioactive-sensitive organs and tissues, like bone-marrow, gastrointestinal tract, as well as central nervous system could occur, which are called the acute radiation syndromes.
And it depends on the part of body to be exposed to radiation, but sometimes skin erythema, hair loss and sterility (temporary or permanent) could occur.
In addition, when exposed women are pregnant, embryo-fetal disorders or mental retardation called fetal disorders could come up with them.
Moreover, it is effects appearing after some time passes after exposure, but cataract or glaucoma could appear, which are called late-onset disorders.
The stochastic effects
So, what are the specific examples of the stochastic effects?
First of all, for the exposed people, late-onset disorders like leukemia or cancer could appear, and as effects on next generation other than the exposed people, it could be possible for the probability for the hereditary effects could increase.
Mechanism to cause the deterministic effects

Let us move on to explanation for the specific mechanisms to cause the deterministic effects, as well as the stochastic effects.
First, the deterministic effects.
Summary of the mechanism is depicted in the above figure, but every single human cell has DNA with genetic information, and part of DNA could be damaged, if they are exposed to radiation.
The damage would be repaired by the curative system which human body inherently has.
Not all damaged DNA, however, could be completely repaired into original condition, but instead part of the damaged DNA could be mistakenly repaired, and some of them could become even dead.
But as long as dose is low and the number of damaged cell is small, it doesn’t cause serious impact on human vital function.
But if dose becomes higher, of course the number of damaged cells also becomes larger, and part of the cells would be correctly repaired, but the number of cells which are mistakenly repaired, or even become dead, will increase, compared with the case of low dose.
Even so, if more than a certain amount of cell is kept intact, vital function of human body will soon be recovered after some time passes, even if temporary loss of vital function could occur.
However, if dose becomes higher and more than a certain level of dose, through death or degeneration of a large amount of cells, vital function of organs or tissues would be lost, or morphological defects could appear, and that could lead to serious impact on human body.
The effects that could cause though the above-mentioned mechanism, are called the deterministic effects, and the dose, which could be a rough indication to assume whether the deterministic effects would appear or not, is called the threshold value or threshold dose.
In other words, the deterministic effects would not appear, even if people are exposed to dose less than the threshold value.
What is the threshold value?
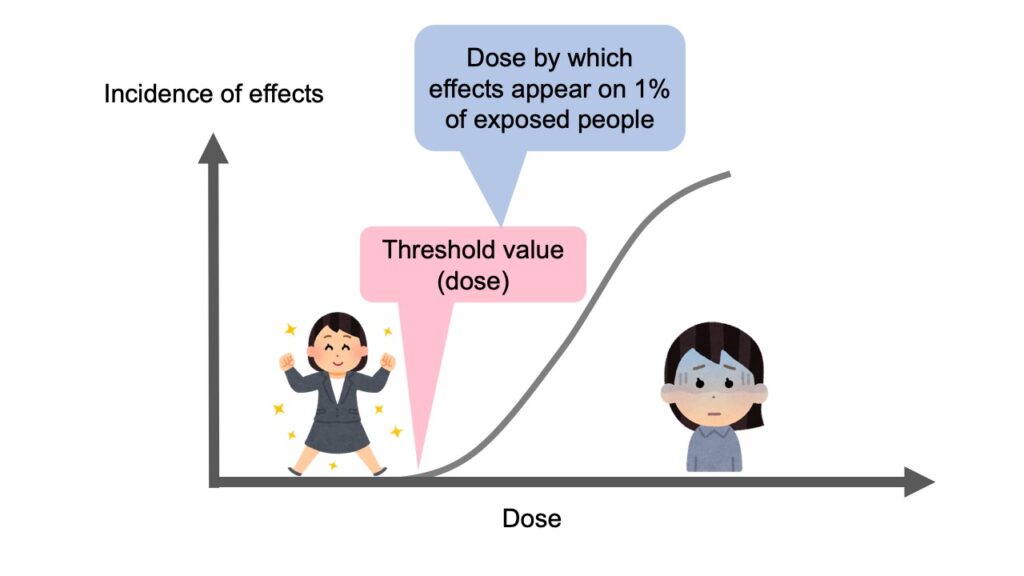
As explained earlier, the threshold dose is a value for the rough indication to know, whether the deterministic effects would appear or not.
If this concept is represented by a graph, it will be like the above figure.
Even if people are exposed to radiation with less than the threshold value, the deterministic effects would not appear, but if people are exposed to radiation with the threshold value or more, incidence of effects would gradually increase, for the deterministic effects to appear on human body.
But please note, that the deterministic effects would appear, necessarily not for all the exposed people, but instead only the incidence of effects would increase.
By the way, the ICRP defines the threshold value as the dose, by which the deterministic effects would appear for 1% of exposed people, provided that a number of people are exposed to the same amount of dose.
Summary
In this article, first it is explained that regarding impact on human health caused by exposure to radiation, there are a couple of approaches for classification of the impacts, followed by introduction for ‘the deterministic effects’ as well as ‘the stochastic effects’, especially focusing on difference of mechanisms to cause the impacts.
Among the effects, regarding the deterministic effects, it was explained that it could appear when people are exposed to radiation with a large amount of radiation, in a relatively short period of time.
In addition, specific symptoms and mechanism to cause the deterministic effects were covered.
And at last, the concept of the threshold value (dose), specific to the deterministic effects is covered.
By the way, above-mentioned contents are summarized in the following videos.
It would be appreciated to visit them at your convenience.
– Japanese version
– English version
You can read the same article in Japanese here.
Thank you very much for reading this article.
See you next time!



コメント