Hello. My name is Daichi, elaborating the radiation issues in an easy-to-understand manner.
In this first article, I would like to respond to the following question(s)/request(s):
– What in all is the atom?
– I’d like to know the basic structure of an atom.
Table of contents of this article
- An atom consists of 3 parts (Its structure is depicted in a figure).
- What is the atom?
- What is the proton?
- What is the neutron?
- What is the electron?
- Summary
I have been involved with the radiation-relevant issues, like the policy on the decontamination activities and the management of the Interim Storage Facility, after the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011.
I received a doctorate in the field of radiation, while working in Fukushima.
An atom consists of 3 parts (Its structure is depicted in a figure).
An example of an atom is shown in the below figure.
This is the structure of the element of helium, which comprises of protons, neutrons and electrons.
At the center of the atom, there are atoms and neutrons, and they are called atom core or nucleus.
You can have an image, that electrons circulate around the atom core.
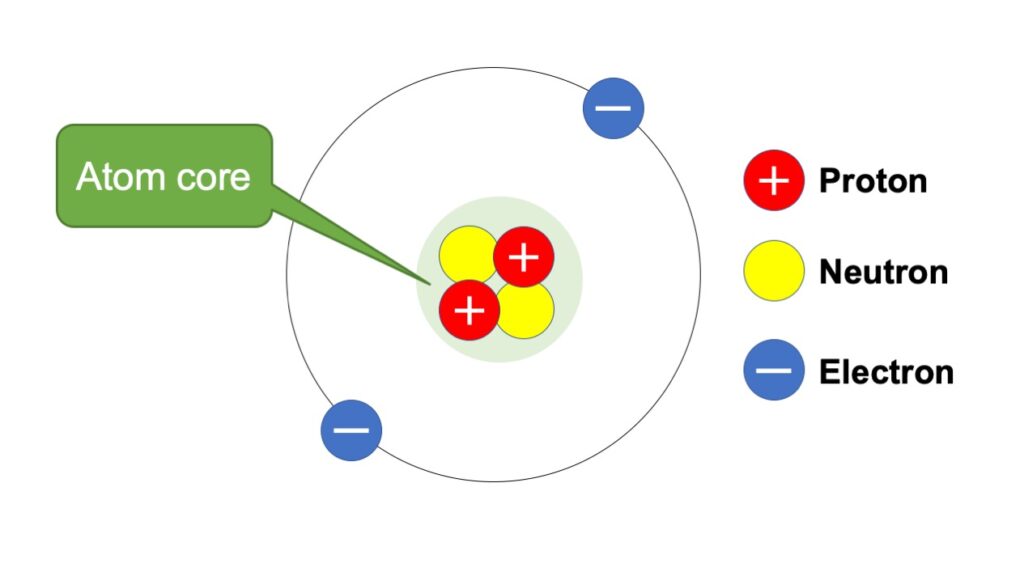
Basic structure of an atom (example of a helium atom)
The atom, as well as three parts consisting of the atom, that is, the proton, the neutron and the electron will be elaborated in the following parts.
What is the atom?
Simply speaking, an atom is the smallest unit of each element (e.g. H: Hydrogen, He: Helium, Li: Lithium).
The element can’t further be physically divided any more.
Actually, the scale of the figure mentioned above is not correct.
The size of the atom is around 10−10m, and the size of the atom core in the center is around (10−15m), one 10 thousandth size of the atom.
Therefore, there is a vast space between the atom core and the edge of the atom.

Frequently the baseball park and one-yen coin or a marble are taken as examples, to represent the size of an atom and an atom core.
What is the proton?
A proton is one of the parts of an atom.
Mass is around 1.6×10−27kg, and it has positive charge.
By the way, the number of proton is atomic number which determines the kind of element.
As shown in the figure, the atom with 2 protons is defined as ‘Helium’, whose atomic number is 2.
What is the neutron?
A neutron is also one of the components of an atom core (protons and neutrons are also called nucleons.)
A neutron is different from an atom, and it is not electrically charged.
Mass of a neutron is slightly larger than a proton, but almost same.
As explained, it is charge-free, therefore, it moves almost straight after leaving an atom core, until it collides with other materials.
By the way, a sum number of protons and neutrons are called a mass number.
For example, the mass number of a helim atom in the figure above is 4, because it has 2 atoms and 2 neutrons.
What is the electron?
An electron circulates on the orbit outside of an atom core.
Its mass is around 1/1680 of an proton, and it is negatively charged.
Usually an atom has the same number of electrons with the number of protons, therefore the charge of an atom remains neutral as a whole.
If electrons are added or removed with some reasons, an atom becomes a particle called an ‘ion’.
Summary
As a first step to understand radiation, structure of the atom was just briefly elaborated.
The articles regarding radiation will come up toward the future, but this is the basis for everything, so it is appreciated, if this is kept in your mind.
By the way, you can read the same article in Japanese here.
Thank you very much for reading this article.
See you next time!



コメント
[…] 本記事の英語版はこちらからご覧いただけます。 […]
[…] To understand radiation, please visit this article. […]