Hello, everyone.
My name is Daichi, an expert providing the information on the radiation issues in an easy-to-understand manner.
Radiation: we can neither see it, hear it nor taste it.
This article will explain what radiation is, and of a lot of kinds of radiation, ionizing radiation will also be covered, which is closely related with human health.
In other words, this article covers the following questions:
– What on earth is radiation?
– What is ionizing radiation?
Table of contents of this article
- (There are 2 definitions) What is radiation?
- What is radiation in a broad sense?
- What is particle beam?
- What is electromagnetic wave?
- What is radiation in a narrow sense?
- What is ionization effect?
- Summary
I have been involved with the radiation-relevant issues, like the policy on the decontamination activities and the management of the Interim Storage Facility, after the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011.
I received a doctorate in the field of radiation, while working in Fukushima.
(There are 2 definitions) What is radiation?
The word ‘radiation’ has two different kinds of meanings: in a broad sense, and in a narrow sense.
Specifically:
– All kinds of particle beams and electromagnetic waves in a broad sense (See ‘What is radiation in a broad sense?’.)
– Ionizing radiation among particle beams and electromagnetic waves (See ‘What is radiation in a narrow sense?’.)
But, when we see or hear the word ‘radiation’, it could often mean ‘ionizing radiation’.
‘Ionization’ will be elaborated in the chapter: ‘What is ionization?’.
Now radiation in a broad/narrow sense will be explained in the following chapters.
What is radiation in a broad sense?
As aforementioned, radiation, in a broad sense, includes all kinds of particle beams and electromagnetic waves.
Then, what is the particle beam and what is the electromagnetic wave?
What is particle beam?

As its word already means, a particle beam is a beam in a particle form migrating through the space.
You can imagine a ball, or group of balls, which fly through the space.
Specifically, for example, alpha particle, beta particle, neutron beam belong to the particle beam.
Regarding the detail of the alpha particle and beta particle, please visit this article, this article, this article and this article.
What is electromagnetic wave?

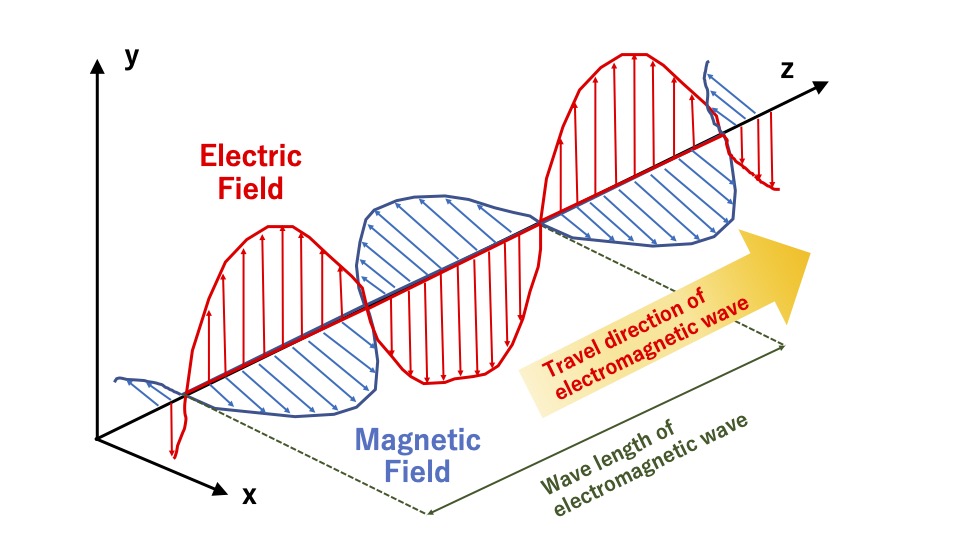
Electromagnetic wave is the wave which migrates through the space, with the successive interaction of magnetic field and electric field.
Some of you might hear the word: ‘electromagnetic induction’.
This is a phenomenon, in which, once magnetic field varies, electric charge moves (the current flows), then magnetic field is influenced by the movement of the electric charge, and further the electric charge moves, and…(same phenomenon continue).
This interaction continues iteratively, and it migrates space: this explains how electromagnetic wave travels the space (See the below figure).
Specifically, for example, gamma ray, X ray, visible light, electric wave belong to electromagnetic wave.
Regarding gamma ray, please visit articles mentioned in the chapter: ‘What is particle beam?’.
What is radiation in a narrow sense?
As mentioned above, radiation in a narrow sense means radiation with ionization effect (ionizing radiation).
So, what is ionization effect?
What is ionization effect?

Ionization effect is a phenomenon, in which orbital electron(s) in an atom core is hit and pushed out of the atom.
An atom or a molecule which loses orbital electron(s) becomes an atom with positive charge, or a cation.
Examples of ionizing radiation (particle beam or electromagnetic wave) are as follows:
– Ionizing radiation (particle beam) e.g.:
Alpha particle, beta particle
– Ionizing radiation (electromagnetic wave) e.g.:
Gamma ray, X-ray
On the other hand, examples of radiation without ionizing effect (non-ionization radiation) are as follows:
– Non-ionizing radiation e.g.:
Visible light, infrared ray, electric wave
By the way, part of the ultraviolet wave has ionizing effect, but generally it is categorized as non-ionizing radiation.
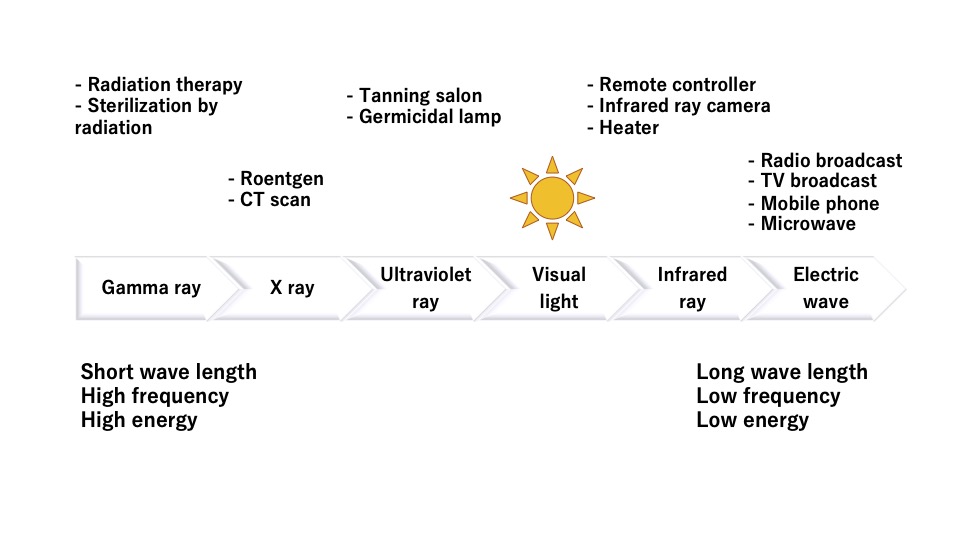
Radiation with ionizing effect has characteristic with short wave length (high frequency) and large energy.
The following figure shows types of electromagnetic wave and a variety of their use.
Summary
Key points of this article are as follows:
– There are two kinds of meanings for the word ‘radiation’: radiation in a broad sense and in a narrow sense.
– ‘Radiation in a broad sense’ means all kinds of particle beams and electromagnetic waves.
– ‘Radiation in a narrow sense’ means ionizing radiation.
By the way, the following videos are created, which explain almost same contents above.
Please take a look at them at your convenience.
– Japanese version
In addition, please also visit the following video recapitulating the same contents within 3 minutes and 1 minute.
<3 minutes>
<1 minute>
– English version
Also for English version, please visit the following video recapitulating the same contents within 3 minutes and 1 minute.
<3 minutes>
<1 minute>
– German version
Only short version within 3 minutes and 1 minute, but the same contents were recapitulated in the following German video.
<3 minutes>
<1 minute>
– French version
Only short version within 1 minute, but the same contents were recapitulated in the following French video.
You can read the same article in Japanese here.
Thank you very much for reading this article.
See you next time!


コメント