Hello, everyone. My name is Daichi, an expert providing the information on the radiation issues in an easy-to-understand manner.
Today, as a continuous work from the previous article, regarding the deterministic effects, I would like to respond to the following questions:
– How much different regarding the impact on each human organ and tissue caused by exposure to radiation?
– What is the impact on fetus caused by exposure to radiation?
Table of contents of this article
- Impact on human health caused by exposure to radiation (Vol. 2)
- Sensitivity of each organ and tissue to radiation
- Impact on fetus caused by exposure to radiation
- Relationship between threshold value and impact on human health
- Summary
I have been involved with the radiation-relevant issues, like the policy on the decontamination activities and the management of the Interim Storage Facility, after the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011.
I received a doctorate in the field of radiation, while working in Fukushima.
Impact on human health caused by exposure to radiation (Vol. 2)
In the previous article, it is explained that there are the deterministic effects and the stochastic effects, as kinds of impact on human health caused by exposure to radiation, and summary of the deterministic effects including its mechanism as well as threshold values are also covered.
This article further covers the threshold values in detail, as well as the rest of the deterministic effects: impact on fetus (fetal disorders).
Sensitivity of each organ and tissue to radiation
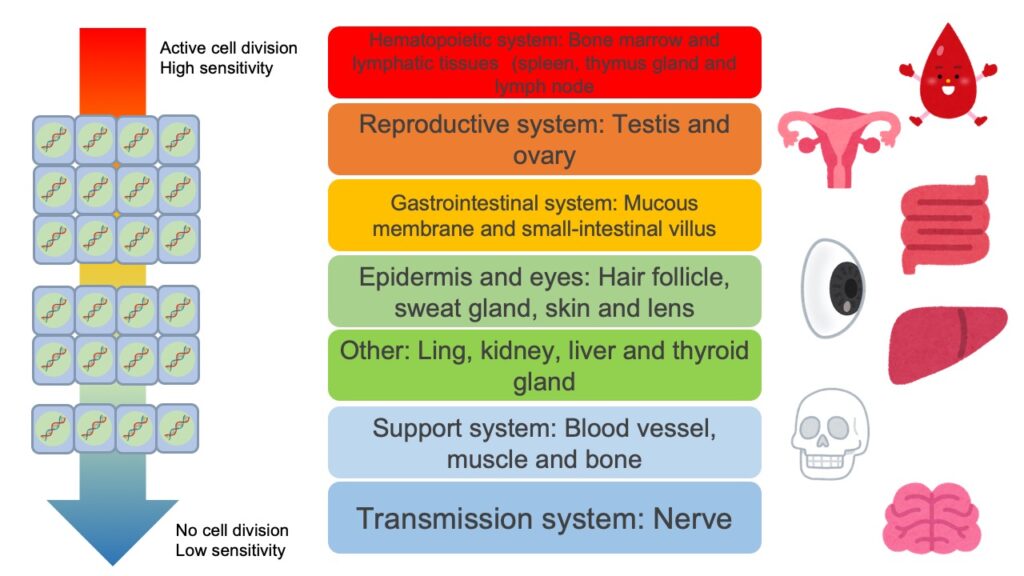
Sensitivity to radiation is different between human organs and tissues.
All human cells generate through differentiation from stem cells and generally speaking, if cells have low differentiation level from stem cells and still more actively divide, they tend to be more sensitive to radiation.
For example, as shown in the above figure, hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow divide very actively, and differentiate into blood cells, like erythrocyte and leucocyte in blood, and they are one of the representative cells with very high sensitivity to radiation.
In testis and ovary, genital cells are frequently and actively produced, and on epithelium of digestive system, cells are always replaced with new ones.
It means, that in these organs and tissues, metabolism is very active and they are also sensitive to radiation.
On the other hand, if differentiation of organs and tissues is already finished, and cells of the organs and tissues don’t divide any more, like muscle and nerve system, it is well-known, that their sensitivity to radiation is generally low.
Specific examples of threshold values are represented in the following table.
For example, if people are exposed to radiation with dose of more than 0.1Gy (100mGy), in a relatively short period of time, temporary sterility could appear: physical phenomena with temporal decrease of the number of sperm.
With exposure to radiation with dose of more than 0.5Gy (500mGy), hemopoietic ability in bone marrow could deteriorate, and the number of cells in blood could decrease.
Although incubation period is long (20 years or longer) compared with other disorders, but negative impact like cataract could appear in the future, with dose of 0.5Gy.
In addition, if people are exposed to radiation with absorbed dose of around 3Gy, permanent sterility for women could appear, and with exposure to radiation of more than around 4Gy, temporary hair loss on skin could occur.
Moreover, with exposure to much higher level of radiation, like absorbed dose of 5-10Gy, possibility of negative effect like skin burn could increase in large area of skin.
| Disorders | Incubation period | Threshold value (Gy, Approx.) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Testis | Temporary sterility | 3 - 9 weeks | 0.1 |
| Bone marrow | Deterioration of hemopoietic ability | 3 - 7 days | 0.5 |
| Eyes | Cataract | 20 years or longer | 0.5 |
| Ovary | Permanent sterility | Within 1 week | 3 |
| Skin | Temporary hair loss | 2 -3 weeks | 4 |
| Skin (large area) | Skin burn | 2 - 3 weeks | 5 - 10 |
Impact on fetus caused by exposure to radiation
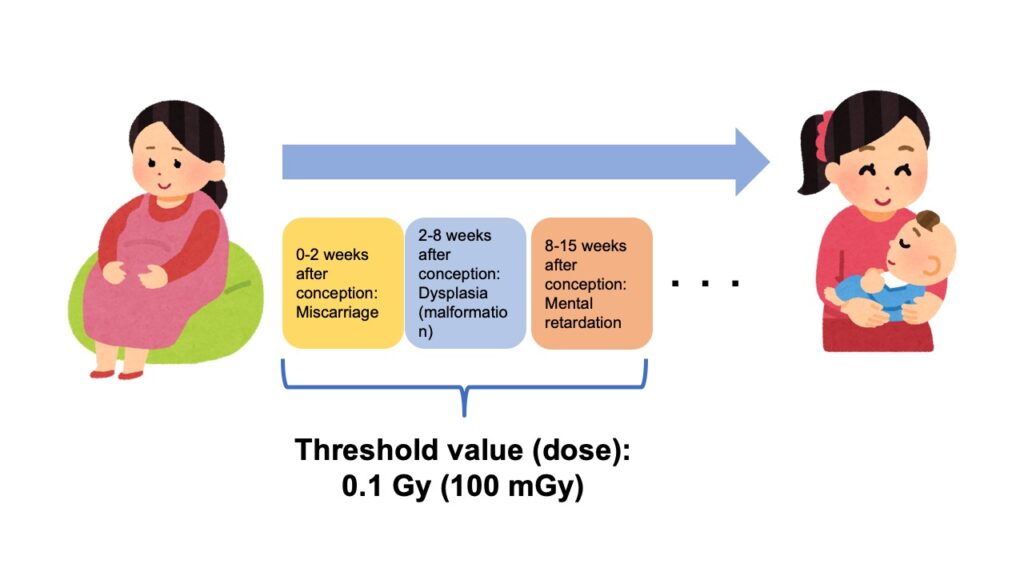
The above-mentioned effects are called the acute disorders or the late-onset disorders, examples of the deterministic effects, as touched on in the previous article.
So, how much is threshold value of the fetal disorders, the rest of the three deterministic effects raised as examples?
Generally speaking, fetus is sensitive to radiation, compared with organs and tissues of adults, because its cells divide very actively.
And if it is exposed to radiation with relatively high dose during early stage after conception, miscarriage could sometimes occur, as shown in the above figure.
Even after the early stage, if it is exposed to radiation while its body is formed, it could be possible, for dysplasia, or mental retardation to fetus to occur.
These deterministic effects on fetus are expected to occur, if it is exposed to radiation with more than 0.1Gy (100mGy) of absorbed dose in a short period of time.
By the way, absorbed dose of 0.1Gy (100mGy) almost correspondents to the same value of effective dose, 0.1Sv (100mSv), when assuming exposure to whole body of people with gamma ray.
Regarding the conversion from the unit of absorbed dose (Gy) to the unit of effective dose (Sv), please visit this article.
Relationship between threshold value and impact on human health

As represented so far, the threshold value of impact caused by exposure to radiation, both for each organ and tissue, as well as for fetus, is 100mGy.
Discussion about threshold value still internationally continues, and there is still possibility for the values to be changed.
However, at this point of time, 100mGy of absorbed dose (almost correspondents to 100mSv of effective dose, under the assumption of exposure to whole body by gamma ray) could be a value to roughly estimate, whether the deterministic effects occur or not.
But as already mentioned, sensitivity to radiation is different between organs and tissues, therefore, especially when it comes to the deterministic effects, it would be better to see details for each organ and tissue.
And please note, that the deterministic effects would not necessarily appear, even if people are exposed to radiation with dose of more than the threshold values, as explained in the previous article.
Summary
Of the deterministic effects, regarding the aforementioned acute disorders and late-onset disorders, this article covered the difference of sensitivity to radiation of each human organ and tissue, with specific examples of threshold values.
And this article also covered the effects on fetus (fetal disorders), the rest of the deterministic effects.
And at last, it could be possible to be reviewed, but it was explained, that the threshold value for the deterministic effects, which has currently become apparent, is around 0.1Gy.
And it was also underlined, that it will be highly likely that the probability for the negative effects to appear, as well as seriousness of disorders will increase/rise, when people are exposed to radiation with dose more than the threshold value, but even in that case, it is not necessarily for the deterministic effects to appear.
By the way, above-mentioned contents are summarized in the following videos.
It would be appreciated to visit them at your convenience.
– Japanese version
– English version
You can read the same article in Japanese here.
Thank you very much for reading this article.
See you next time!


コメント